Operational Analysis
Indra deploys its technological solutions for operational analysis as a key capability for national sovereignty and as a systematic process that connects strategic vision and mission needs with the design of effective solutions.
It is the essential tool for transforming military strategic needs into clear requirements.
Decision-making supported by mathematical analysis and simulation
Operational analysis enables evidence-based decision-making through scientific methods, mathematical analysis and simulation testing, helping to determine the capabilities required to strengthen a nation’s defence and ensure that launched programmes meet established requirements.
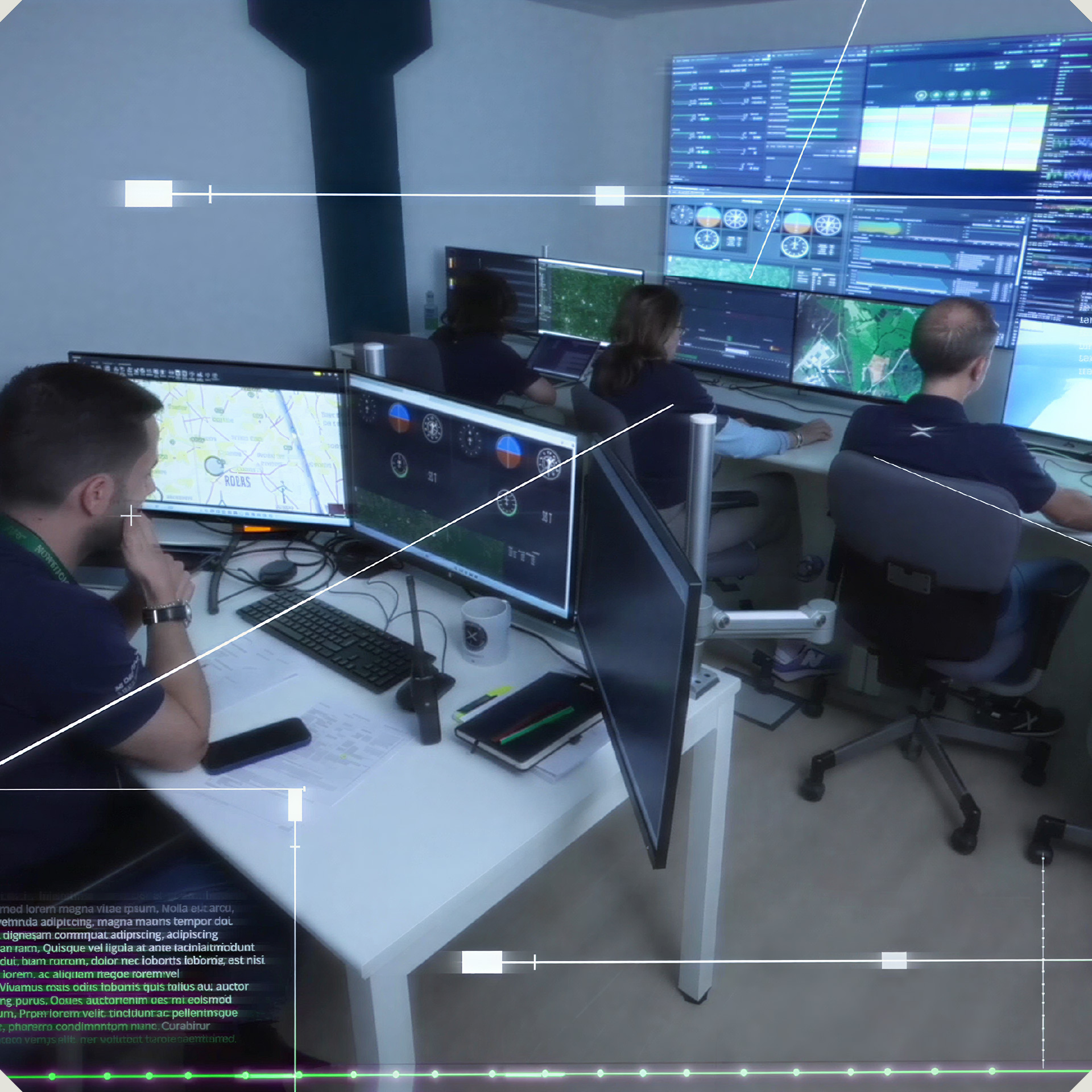
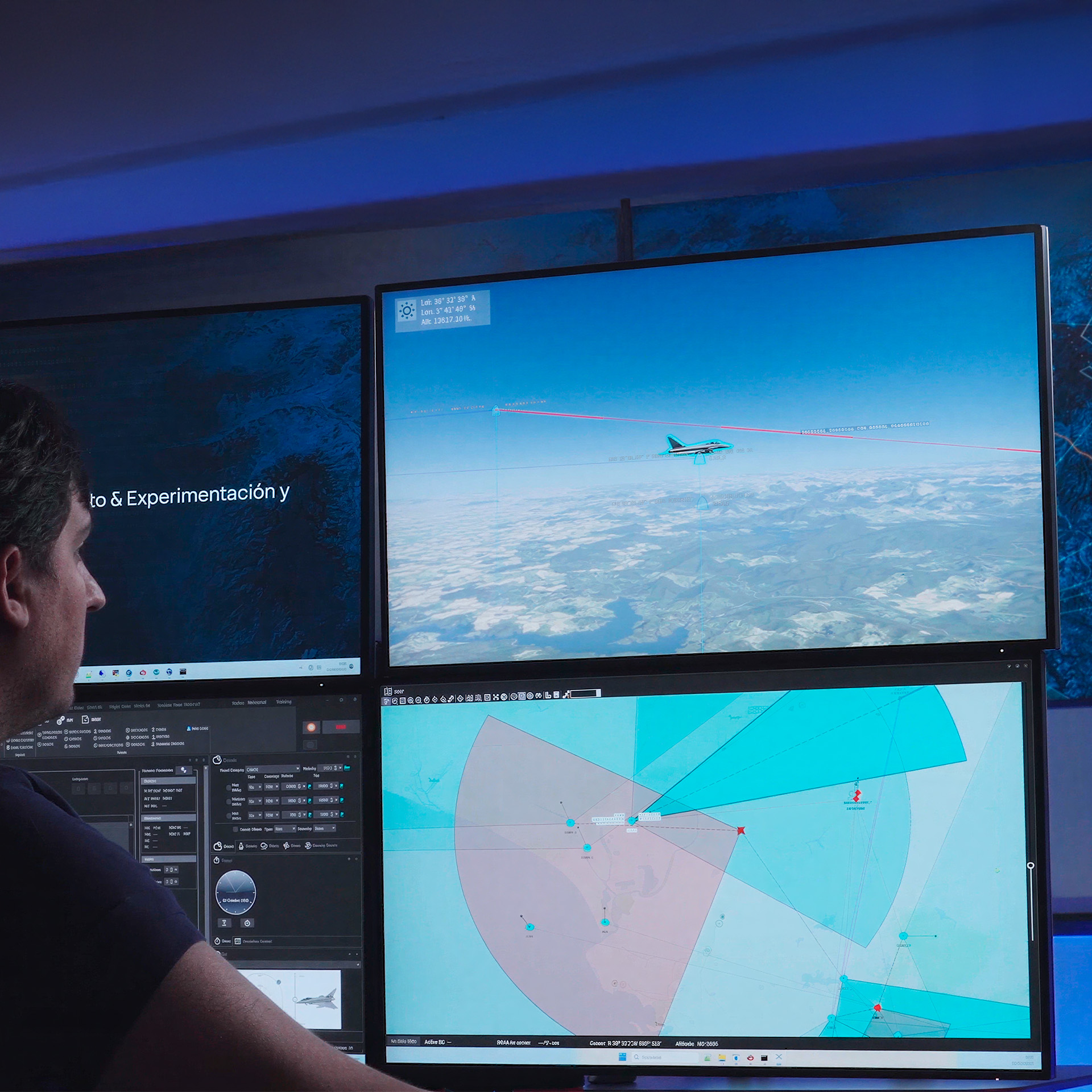
It also allows the synthetic reproduction of air, naval, land, and even multi-domain combat scenarios, while integrating current real systems, and conducting hundreds of exercises to test different system configurations under varying environmental conditions, using diverse operational strategies.
Pre-analysis of systems and operations using these techniques makes it possible to set clear specifications for prototype development that meet the Armed Forces’ defined needs, reducing development times and avoiding cost overruns caused by requirement changes during the project. Likewise, this type of analysis identifies the capabilities an army needs and the best options to fulfil them.
In this way, the innovation cycle is accelerated, system design is optimised, and the most effective technologies are selected.
- Stakeholder analysis and their needs
- Identification and prioritisation of capabilities
- Scenario modelling and Concept of Operations (CONOPS)
- Definition of measurable operational requirements (MOE and MOP)
- Evaluation of Alternatives (AoA) to ensure the optimal solution


Prevention, strategy, optimisation, interoperability, and performance
Early error prevention: detection of inconsistencies, technical risks and capability gaps before the design phase, when correcting them has the least economic and schedule impact.
Reduction of 20–30% in defects during integration phases, thanks to improved requirements traceability and early validation.
Improved interoperability and performance: integration of trade-off and scenario analysis (wargaming, simulations), ensuring maximum operational effectiveness.
Every euro invested in Operational Analysis can prevent up to €10–15 in cost overruns during the system’s life cycle.
Cost and schedule optimisation: reducing budget and timeline deviations through precise definition of operational requirements.
Reduction of up to 25% in time-to-market, thanks to early detection of bottlenecks and better prioritisation of capabilities.
Cost and Schedule Optimisation: reducing budget and timeline deviations through a precise definition of operational requirements.
Applying a full Operational Analysis at the start of projects results in a 30–40% reduction in cost overruns.
Standardised approach: based on INCOSE best practices and international standards (ISO-15288).

Contact us